


A firm is most productively efficient at the lowest average total cost, which is also where average total cost (ATC) = marginal cost (MC).When marginal cost is below average total cost, average total cost will be falling, and when marginal cost is above average total cost, average total cost will be rising.Marginal cost will always cut average total cost from below.The general rules governing the relationship are: The lowest price a firm is prepared to supply at is the price that just covers marginal cost.Īverage total cost and marginal cost are connected because they are derived from the same basic numerical cost data.It is the leading cost curve, because changes in total and average costs are derived from changes in marginal cost.The marginal cost curve is significant in the theory of the firm for two reasons:
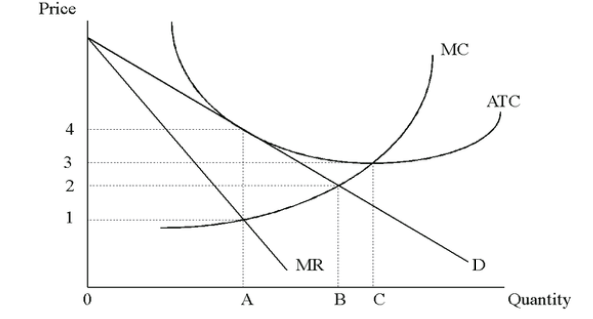
Marginal costs are derived from variable costs and are subject to the principle of variable proportions. The marginal cost curve falls briefly at first, then rises. It is important to note that marginal cost is derived solely from variable costs, and not fixed costs. It can be found by calculating the change in total cost when output is increased by one unit. Marginal cost is the cost of producing one extra unit of output. Total Fixed costs and Total Variable costs are the respective areas under the Average Fixed and Average Variable cost curves. The ATC curve is also ‘U’ shaped because it takes its shape from the AVC curve, with the upturn reflecting the onset of diminishing returns to the variable factor. OUTPUTĪverage total cost (ATC) can be found by adding average fixed costs (AFC) and average variable costs (AVC). Average variable costs are found by dividing total fixed variable costs by output. Average total costs are a key cost in the theory of the firm because they indicate how efficiently scarce resources are being used. Diminishing returns, which cause costs to rise.Īverage total cost (ATC) is also called average cost or unit cost.Increasing returns to the variable factors, which cause average costs to fall, followed by:.The average variable cost (AVC) curve will at first slope down from left to right, then reach a minimum point, and rise again.ĪVC is ‘U’ shaped because of the principle of variable Proportions, which explains the three phases of the curve: Average variable costsĪverage variable costs are found by dividing total fixed variable costs by output. The average fixed cost (AFC) curve will slope down continuously, from left to right. As fixed cost is divided by an increasing output, average fixed costs will continue to fall. Average fixed costsĪverage fixed costs are found by dividing total fixed costs by output. Its position reflects the amount of fixed costs, and its gradient reflects variable costs. The total cost (TC) curve is found by adding total fixed and total variable costs. The total variable cost (TVC) curve slopes up at an accelerating rate, reflecting the law of diminishing marginal returns. Given that total fixed costs (TFC) are constant as output increases, the curve is a horizontal line on the cost graph. Plotting this gives us Total Cost, Total Variable Cost, and Total Fixed Cost. Total variable costs (TVC) will increase as output increases. The total fixed costs, TFC, include premises, machinery and equipment needed to construct boats, and are £100,000, irrespective of how many boats are produced. Consider the following hypothetical example of a boat building firm.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
